- Home
- Medical Imaging
- Molecular Imaging
- MI Trends and Innovations
- SPECT/CT in musculoskeletal medicine

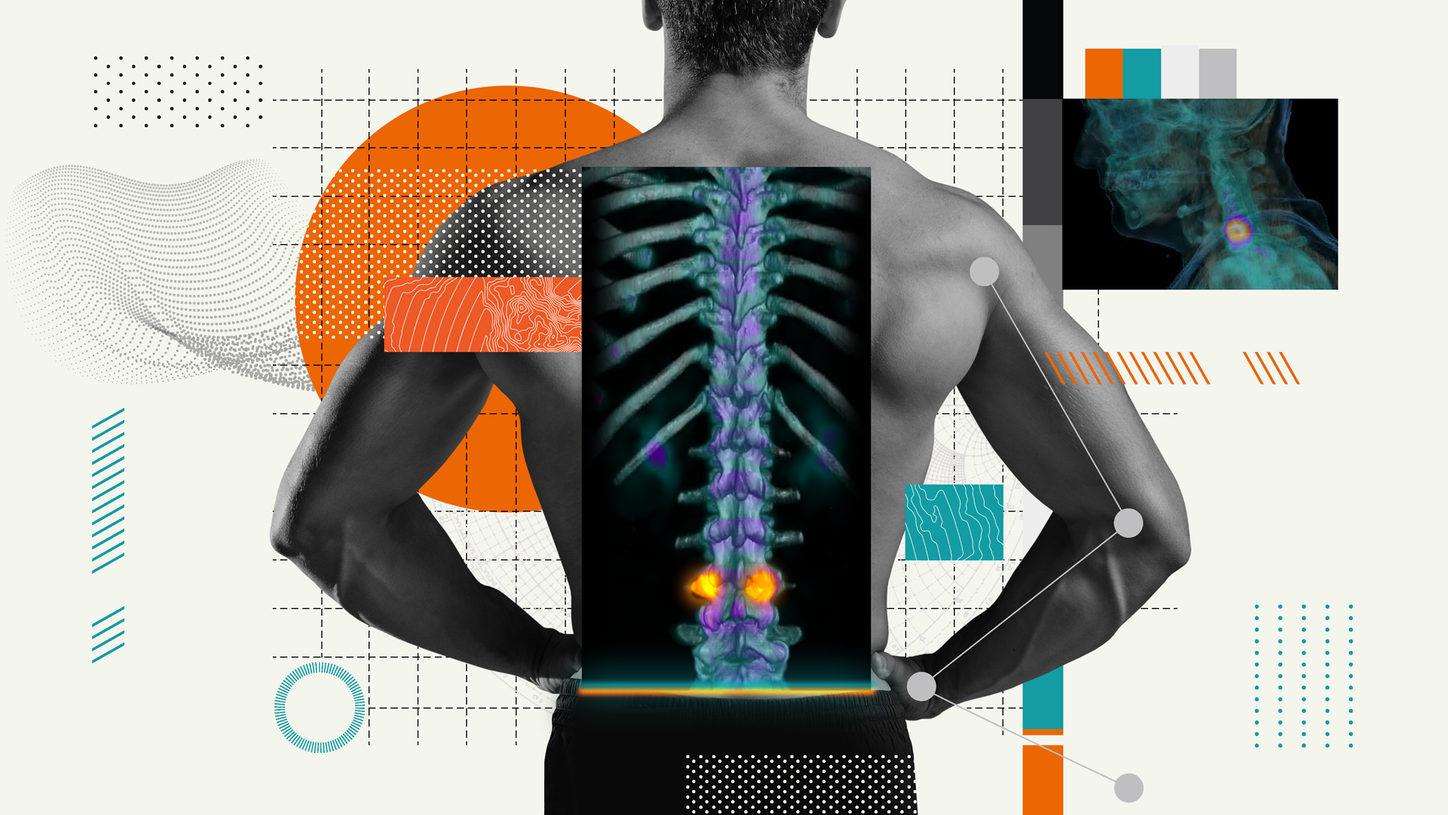
SPECT/CT in musculoskeletal medicinePinpoint musculoskeletal pain with precision
Whether genetic, age-related, or trauma-induced, diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries and conditions can be difficult. 2D imaging demonstrates clinical utility in the anatomical evaluation of musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders, but is it providing you with enough specificity to accurately identify pain generators?
Combining both physiological and anatomical information, 3D SPECT/CT is your one-stop tool for quickly pinpointing the source of musculoskeletal pain and confirming the presence of disease with precision—possibly reducing the need for exploratory surgery or other diagnostic procedures.
What the experts are saying
Read physicians' experience with using SPECT/CT for MSK disorders.
“The 2D CT, X-ray, and MRI images are of great help in orthopedic practice, but SPECT/CT images reconstructed with xSPECT Bone and viewed on syngo.via add valuable information and increase diagnostic confidence. Not all osteoblastic bone activity showcased is abnormal activity. As a result, in some cases, unnecessary surgery can be avoided...”

Gouda, The Netherlands
“X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans give us anatomic detail that can show whether there are potential pain generators. SPECT gives us physiological information, so it tells us if a particular area of degenerative arthritis (osteoarthritis) is physiologically active. The more degenerative a joint is, the higher chance we will see increased metabolic activity in that joint.”

Blacksburg, Virginia, USA
Clinical Use
Clinical image review
View nuclear medicine clinical images in this series of clinical case studies.

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
SPECT/CT shows leukocyte accumulation in stabilization screws of intramedullary rod inserted for femoral fracture
- Patient with bilateral femoral intramedullary rod insertion secondary to fracture
- 99mTc-labeled white blood cell (WBC) SPECT/CT shows focal accumulation of radiolabeled-WBCs at the insertion of the upper stabilization screw into the right intramedullary rod suggestive of infection at screw insertion
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact related to stabilization pin for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism at pin insertion
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 5i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled leukocytes 8.91 mCi (330 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/150 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Bone SPECT fused with CT defines severe degenerative endplate changes in cervical vertebrae
- Patient with neck pain underwent a bone SPECT/CT
- SPECT/CT shows hypermetabolism in the endplates of the C5-C6 vertebrae
- CT shows severe degenerative changes in the vertebral endplates with a reduction of disk space, endplate osteophyte formation, endplate sclerosis, as well as subcortical cystic changes
- Hypermetabolism on SPECT correlates with degenerative endplate changes on CT
- Thin-slice CT with Tin Filter accurately defines details of endplate erosion along with osteophyte and subcortical cyst formation
Symbia Pro.specta™ SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 32 stops per detector, 13 seconds per stop
Total scan time: ~7 minutes
Image reconstruction: 256 x 256 matrix, Flash 3D, 18i4s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV Sn/251 ref mAs, 0.8-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR464 S3

Data courtesy of St Paul's Hospital, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
Bone SPECT fused with CT with iMAR defines non-union of talo-calcaneal joint arthrodesis
- Patient with fracture of left ankle and fibula underwent fixation of lower end of tibia and talus using two fixation screws
- SPECT/CT shows hypermetabolism with joint space erosion in the talo-calcaneal joint space, reflecting failure of arthrodesis fusion
- CT with Tin Filter with iMAR1 provides metal-artifact-free images for sharp delineation of fixation screws and detail of joint space erosion and adjacent focal lytic changes within talus and calcaneus
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 64 stops per detector, 15 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 16 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 18i4s
Injected dose: 99mTc-MDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV Sn/190 ref mAs, 0.8-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 0.8-mm recon, BR464 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone fused with CT with iMAR defines L4 facet arthropathy adjacent to spinal stabilization screw
- xSPECT Bone™ shows focal hypermetabolism in the left L3/4 facet joint with loss of joint space, subchondral sclerosis, and subchondral cyst formation consistent with accelerated osteoarthritis
- Spinal stabilization rods and screws show normal tracer uptake
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifacts related to spinal screws for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism related to the screw tips
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 2 bed positions/60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 40 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 16.4 mCi (610 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-second rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
Bone SPECT/CT defines site of fracture of vertical spinal stabilization rod at level of L5 vertebral pedicle
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows intense focal hypermetabolism at the base of left lower pedicle screw attaching the left spinal stabilization rod with the body of the L5 vertebrae related to fracture of right vertical rod
- Fracture of left S1 interpedicular screw with loosening of left trans-sacroiliac joint screw is also associated with focal hypermetabolism
- Significant scoliosis involving the lumbar vertebrae with associated degenerative changes in the vertebral end plates
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 3 bed positions/60 stops per detector, 10 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 30 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 7i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 20.9 mCi (776 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV/30 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation,1.5-mm recon, BR40 S3

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone fused with CT with iMAR defines bone stress in lateral aspect of femoral component of knee arthroplasty
- xSPECT Bone™ shows sharply defined hypermetabolism with high contrast in lateral aspect of femoral component of total knee arthroplasty involving the right knee reflecting bone stress
- CT with iMAR1 provides metal-artifact-free images for accurate fusion with xSPECT Bone for proper localization of hypermetabolism at prosthesis bone interface
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 15.3 mCi (569 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone delineates arthritic changes in ankle and tarsal joints bilaterally
- xSPECT Bone™ shows hypermetabolism in both ankle joints along with sclerosis of articular surfaces and joint space reduction typical of arthritic changes
- Right talocalcaneal joint shows severe articular surface erosion with corresponding hypermetabolism suggesting severe arthritis
- Arthritis changes also in joint surface between talus and cuneiforms
- Thin-slice CT clearly defines articular erosion and sclerosis
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 15.3 mCi (568 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows bone remodeling around stem of femoral component of knee arthroplasty
- Post-trauma total knee arthroplasty (TKA) with pain on weight-bearing knee
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows focal hypermetabolism around the junction of the stem and body of the femoral component of TKA suggestive of reactive changes secondary to bone remodeling
- Photopenic area at the tip of the femoral stem corresponds to sclerotic bone reflecting cortical thickening and sclerosis around prosthesis related to fracture union
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 7 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 7 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, Flash 3D, 5i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/150 eff mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone and CT with iMAR define reactive bony sclerosis in tibial malunion following plate fixation
- Traumatic open fracture of the lower third of the shaft of the left tibia treated with plate and screw fixation
- Malunion of the tibial shaft despite fixation
- xSPECT Bone™ delineates hypermetabolism localized to thickened sclerosed cortical bone at site of malunion towards the middle of the fixation plate
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact caused by fixation plate for clear visualization of cortical sclerosis as well as bent tibial plate secondary to malunion
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 16.3 mCi (603 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 120 kV/150 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
Bone SPECT/CT shows reactive changes around stem and humeral joint surface of bilateral shoulder arthroplasty
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT in a patient with resurfacing hemi-arthroplasty of both shoulders
- The joint surface of humeral head replaced with a cap-like prosthesis
- Glenoid left intact with resurfacing
- SPECT/CT shows reactive hypermetabolism in the stem and humeral joint surface of bilateral shoulder joint prosthesis without evidence of loosening
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact related to humeral component of prosthesis for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism at humeral joint surface
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 10 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 10 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 7i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 120 kV/105 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
SPECT/CT shows leukocyte accumulation in stabilization screws of intramedullary rod inserted for femoral fracture
- Patient with bilateral femoral intramedullary rod insertion secondary to fracture
- 99mTc-labeled white blood cell (WBC) SPECT/CT shows focal accumulation of radiolabeled-WBCs at the insertion of the upper stabilization screw into the right intramedullary rod suggestive of infection at screw insertion
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact related to stabilization pin for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism at pin insertion
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 5i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled leukocytes 8.91 mCi (330 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/150 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Bone SPECT fused with CT defines severe degenerative endplate changes in cervical vertebrae
- Patient with neck pain underwent a bone SPECT/CT
- SPECT/CT shows hypermetabolism in the endplates of the C5-C6 vertebrae
- CT shows severe degenerative changes in the vertebral endplates with a reduction of disk space, endplate osteophyte formation, endplate sclerosis, as well as subcortical cystic changes
- Hypermetabolism on SPECT correlates with degenerative endplate changes on CT
- Thin-slice CT with Tin Filter accurately defines details of endplate erosion along with osteophyte and subcortical cyst formation
Symbia Pro.specta™ SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 32 stops per detector, 13 seconds per stop
Total scan time: ~7 minutes
Image reconstruction: 256 x 256 matrix, Flash 3D, 18i4s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV Sn/251 ref mAs, 0.8-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR464 S3

Data courtesy of St Paul's Hospital, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
Bone SPECT fused with CT with iMAR defines non-union of talo-calcaneal joint arthrodesis
- Patient with fracture of left ankle and fibula underwent fixation of lower end of tibia and talus using two fixation screws
- SPECT/CT shows hypermetabolism with joint space erosion in the talo-calcaneal joint space, reflecting failure of arthrodesis fusion
- CT with Tin Filter with iMAR1 provides metal-artifact-free images for sharp delineation of fixation screws and detail of joint space erosion and adjacent focal lytic changes within talus and calcaneus
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 64 stops per detector, 15 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 16 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 18i4s
Injected dose: 99mTc-MDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV Sn/190 ref mAs, 0.8-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 0.8-mm recon, BR464 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone fused with CT with iMAR defines L4 facet arthropathy adjacent to spinal stabilization screw
- xSPECT Bone™ shows focal hypermetabolism in the left L3/4 facet joint with loss of joint space, subchondral sclerosis, and subchondral cyst formation consistent with accelerated osteoarthritis
- Spinal stabilization rods and screws show normal tracer uptake
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifacts related to spinal screws for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism related to the screw tips
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 2 bed positions/60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 40 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 16.4 mCi (610 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-second rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
Bone SPECT/CT defines site of fracture of vertical spinal stabilization rod at level of L5 vertebral pedicle
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows intense focal hypermetabolism at the base of left lower pedicle screw attaching the left spinal stabilization rod with the body of the L5 vertebrae related to fracture of right vertical rod
- Fracture of left S1 interpedicular screw with loosening of left trans-sacroiliac joint screw is also associated with focal hypermetabolism
- Significant scoliosis involving the lumbar vertebrae with associated degenerative changes in the vertebral end plates
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 3 bed positions/60 stops per detector, 10 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 30 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 7i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 20.9 mCi (776 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 130 kV/30 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation,1.5-mm recon, BR40 S3

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone fused with CT with iMAR defines bone stress in lateral aspect of femoral component of knee arthroplasty
- xSPECT Bone™ shows sharply defined hypermetabolism with high contrast in lateral aspect of femoral component of total knee arthroplasty involving the right knee reflecting bone stress
- CT with iMAR1 provides metal-artifact-free images for accurate fusion with xSPECT Bone for proper localization of hypermetabolism at prosthesis bone interface
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 15.3 mCi (569 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone delineates arthritic changes in ankle and tarsal joints bilaterally
- xSPECT Bone™ shows hypermetabolism in both ankle joints along with sclerosis of articular surfaces and joint space reduction typical of arthritic changes
- Right talocalcaneal joint shows severe articular surface erosion with corresponding hypermetabolism suggesting severe arthritis
- Arthritis changes also in joint surface between talus and cuneiforms
- Thin-slice CT clearly defines articular erosion and sclerosis
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 15.3 mCi (568 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/181 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows bone remodeling around stem of femoral component of knee arthroplasty
- Post-trauma total knee arthroplasty (TKA) with pain on weight-bearing knee
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT shows focal hypermetabolism around the junction of the stem and body of the femoral component of TKA suggestive of reactive changes secondary to bone remodeling
- Photopenic area at the tip of the femoral stem corresponds to sclerotic bone reflecting cortical thickening and sclerosis around prosthesis related to fracture union
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 7 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 7 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, Flash 3D, 5i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/150 eff mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
xSPECT Bone and CT with iMAR define reactive bony sclerosis in tibial malunion following plate fixation
- Traumatic open fracture of the lower third of the shaft of the left tibia treated with plate and screw fixation
- Malunion of the tibial shaft despite fixation
- xSPECT Bone™ delineates hypermetabolism localized to thickened sclerosed cortical bone at site of malunion towards the middle of the fixation plate
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact caused by fixation plate for clear visualization of cortical sclerosis as well as bent tibial plate secondary to malunion
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, xSPECT Bone
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP 16.3 mCi (603 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 3 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 120 kV/150 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
Bone SPECT/CT shows reactive changes around stem and humeral joint surface of bilateral shoulder arthroplasty
- 99mTc-HMDP bone SPECT/CT in a patient with resurfacing hemi-arthroplasty of both shoulders
- The joint surface of humeral head replaced with a cap-like prosthesis
- Glenoid left intact with resurfacing
- SPECT/CT shows reactive hypermetabolism in the stem and humeral joint surface of bilateral shoulder joint prosthesis without evidence of loosening
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact related to humeral component of prosthesis for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism at humeral joint surface
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 10 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 10 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 7i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMDP (dose amount anonymized)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 120 kV/105 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR

Data courtesy of Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
SPECT/CT shows leukocyte accumulation in stabilization screws of intramedullary rod inserted for femoral fracture
- Patient with bilateral femoral intramedullary rod insertion secondary to fracture
- 99mTc-labeled white blood cell (WBC) SPECT/CT shows focal accumulation of radiolabeled-WBCs at the insertion of the upper stabilization screw into the right intramedullary rod suggestive of infection at screw insertion
- CT with iMAR1 eliminates metal artifact related to stabilization pin for clear visualization and localization of hypermetabolism at pin insertion
Symbia Pro.specta SPECT/CT
SPECT
Scan acquisition: 60 stops per detector, 20 seconds per stop
Total scan time: 20 minutes
Image reconstruction: 128 x 128 matrix, OSEM3D, 5i15s
Injected dose: 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled leukocytes 8.91 mCi (330 MBq)
Post-injection delay: 2 hours
CT
SAFIRE
Scan parameters: 110 kV/150 ref mAs, 0.33-sec rotation, 32 x 0.7-mm collimation, 1-mm recon, BR44 S3 iMAR










Scientific Presentations
Learn new insights from a collection of scientific presentations from critically acclaimed physicians in the field of MSK medicine.

Clinical experience of routine SPECT/CT reading after migrating from Symbia.net to syngo.via
Dr. Iain Duncan
Garran Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia

Efficiency by routine: MSK xSPECT/CT
Dr. Human Adams
Green Heart Hospital, Gouda, The Netherlands

Orthopedic view on utilizing SPECT/CT in clinical practice
Dr. Helmut Rasch
Kantonsspital Baselland

Our experience using xSPECT/CT bone in musculoskeletal medicine
Dr. Iain Duncan
Garran Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia

Clinical experience of routine SPECT/CT reading after migrating from Symbia.net to syngo.via
Dr. Iain Duncan
Garran Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia

Efficiency by routine: MSK xSPECT/CT
Dr. Human Adams
Green Heart Hospital, Gouda, The Netherlands

Orthopedic view on utilizing SPECT/CT in clinical practice
Dr. Helmut Rasch
Kantonsspital Baselland

Our experience using xSPECT/CT bone in musculoskeletal medicine
Dr. Iain Duncan
Garran Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia

Clinical experience of routine SPECT/CT reading after migrating from Symbia.net to syngo.via
Dr. Iain Duncan
Garran Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia




News & Stories
Read more about musculoskeletal medicine and orthopedics in these Nuclear Medicine News & Stories articles.

The use of SPECT/CT in a musculoskeletal Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation practice

The convergence of nuclear medicine and orthopedic surgery

The convergence of nuclear medicine and pediatric orthopedic surgery
The convergence of nuclear medicine and musculoskeletal medicine