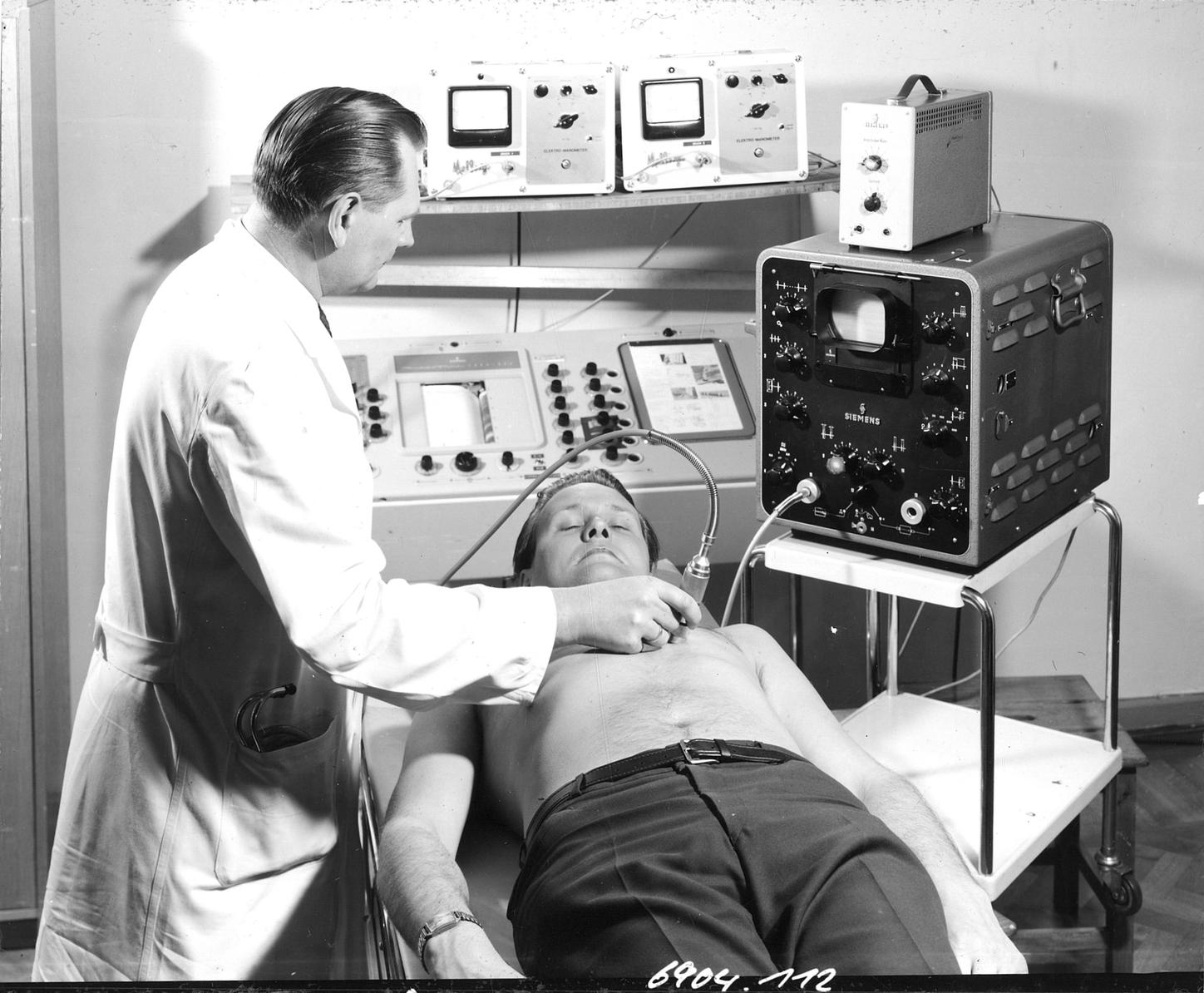
1938
Reimar Pohlman began a series of experiments on the medical use of ultrasound in patients with sciatica and neuralgia at Berlin’s Martin Luther Hospital. The very next year, he went to work in research and development for Siemens.
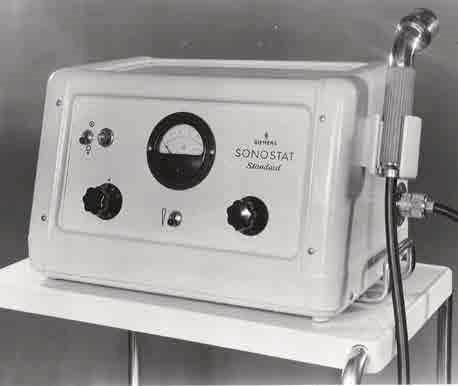
1947
The first therapeutic ultrasound devices, such as the SONOSTAT, were created starting in 1947. From 1968, ultrasound was used not just in physical therapy, but also in urology, where the technique was first used to destroy bladder stones.

1951
A Siemens ultrasound reflectoscope for material testing of steel plates was used e.g. in shipyards. The ultrasound devices of this period were produced by the Siemens- Reiniger-Werke (SRW).
1953
In October 1953, Dr. Inge Edler and Dr. Carl Hellmuth Hertz of Lund University in Sweden took the first images of movements of the heart with ultrasound waves using the material testing system from Siemens. The new method, today known as echocardiography, became an essential part of cardiac diagnosis.

1963
Krautkrämer’s Echo- Encephalograph was the first ultrasound diagnostic device for examination of the brain. It could be used to detect brain hemorrhages after accidents and other abnormal processes in the brain.
1967
The Vidoson, the world’s first real-time ultrasound system, was clinically tested in the mid-1960s. The system’s real-time cross-section imaging acquisition was immediately adopted by physicians, making real-time ultrasound the most widely used imaging modality in virtually every branch of medicine.

1977/1978
The first compound scanner for sectional ultrasound images from Siemens is the TOMOSON.

1979
Siemens introduced the first computer-controlled automatic real-time-scanner, the Diasonics RA-1. The system could take real-time images and compound scans. The RA-1 combined automatic image capture and digital image processing for the first time, reducing scan time considerably while taking higher resolution images.
1979
Siemens launched the Echopan KS with sector scanner and innovative transducer. It was the first Siemens echocardiography system that was able to display real-time images of the heart in B mode.

1982
SONOLINE 1000 was the first portable ultrasound system from Siemens. It weighed only 10 kg and could be taken along by doctors visiting patients at their homes. It was mainly used for obstetrics and gynecology and featured real-time and time-motion imaging.

1983
SONOLINE SL was the first combined ultrasound system for linear arrays and mechanical sector scanning. It could be used for cardiology, obstetrics and organ diagnosis. Images could be stored on a VHS video recorder.
1983
ACUSON Corporation (taken over by Siemens in 2000) marketed its first ever product, the ACUSON 128 as a device for “Computed Sonography™”. Its analog/digital hybrid computer with 128 image resolution channels made automatic image quality control a reality and allowed easy software upgrades to future features.

1988/1989
The SONOLINE CF echo- cardiography scanner for color flow imaging, developed by Siemens, was especially simple to handle thanks to its windowing technique.
1990
The ultrasound device Q2000 was the first Siemens system with color Doppler technology. It made the imaging of blood flow in vessels possible for the first time without invasive peripheral angiography. The Q2000 was able to display anatomical features in black and white and blood flow in color simultaneously, thanks to a super-fast microprocessor with 500 million operations per second.

1995
SONOLINE Prima was the first ultrasound system with digital workflow from Siemens.

1995/1996
Siemens introduced SONOLINE Elegra, the first fully digital ultrasound device of the SONOLINE product line. Its digital image processing enabled the user to choose up to double the number of focus points compared to an analog ultrasound system and better signal processing which allowed the differentiation of very small changes in tissues.

1996
The introduction of the ACUSON Sequoia system provided clinicians with twice the information in half the time. For the first time ever, an ultrasound system was able to use both the phase and the amplitude information of the sound signal. Known as Coherent Image Formation this technology became state-of-the-art for ultrasound imaging offering unprecedented spatial and temporal image resolution.

1997
The software SieScape, fully integrated in the high end ultrasound device SONOLINE Elegra, allowed users for the first time worldwide to immediately view structures and internal organs measuring up to 60 cm across with a high-resolution real-time ultrasound unit in a single image. Images were acquired with a standard probe without a position sensor, enabling the physician to obtain cross sections by simply moving the probe over the surface of the body.

1999
The software “3-Scape Real-Time 3D” was the first high-resolution three dimensional real-time software from Siemens. It could be used with conventional transducers and allowed to process and display 3D-images of anatomical features. This proved especially useful in obstetrics and gynecology with fetus movements impeding diagnosis.

2000
Siemens introduced the first ultrasound catheter AcuNav to visualize the entire heart. Its size of 10 French enables improved access for heart applications in electrophysiology and interventional cardiology.

2001
SONOLINE Antares was the smallest and lightest premium ultrasound device to date.

2003
Siemens presented the first portable ultrasound machine for echocardiography, the ACUSON Cypress. The machine was even used to measure the effects of extreme altitude on heart and lung function during an expedition to Mount Everest in 2003.

2004
The invention of 4-dimensional ultrasound imaging technology allowed the real-time display of three dimensional images for the first time. This provided physicians with moving images, increasing the available diagnostic information, especially for obstetrics, abdominal and vascular imaging.

2005
With a new generation of ultrasound contrast media – microscopically small gas bubbles – and with the help of the CPS technology in Siemens ultrasound systems, physicians can track cancer and metastases. These micro-bubbles are injected into the patient’s vein from where they circulate around the body – and start to concentrate in characteristic patterns in suspicious areas. The agent can even highlight areas not previously detected. At this time, the new method was first used to diagnose liver cancer and other liver lesions.

2007
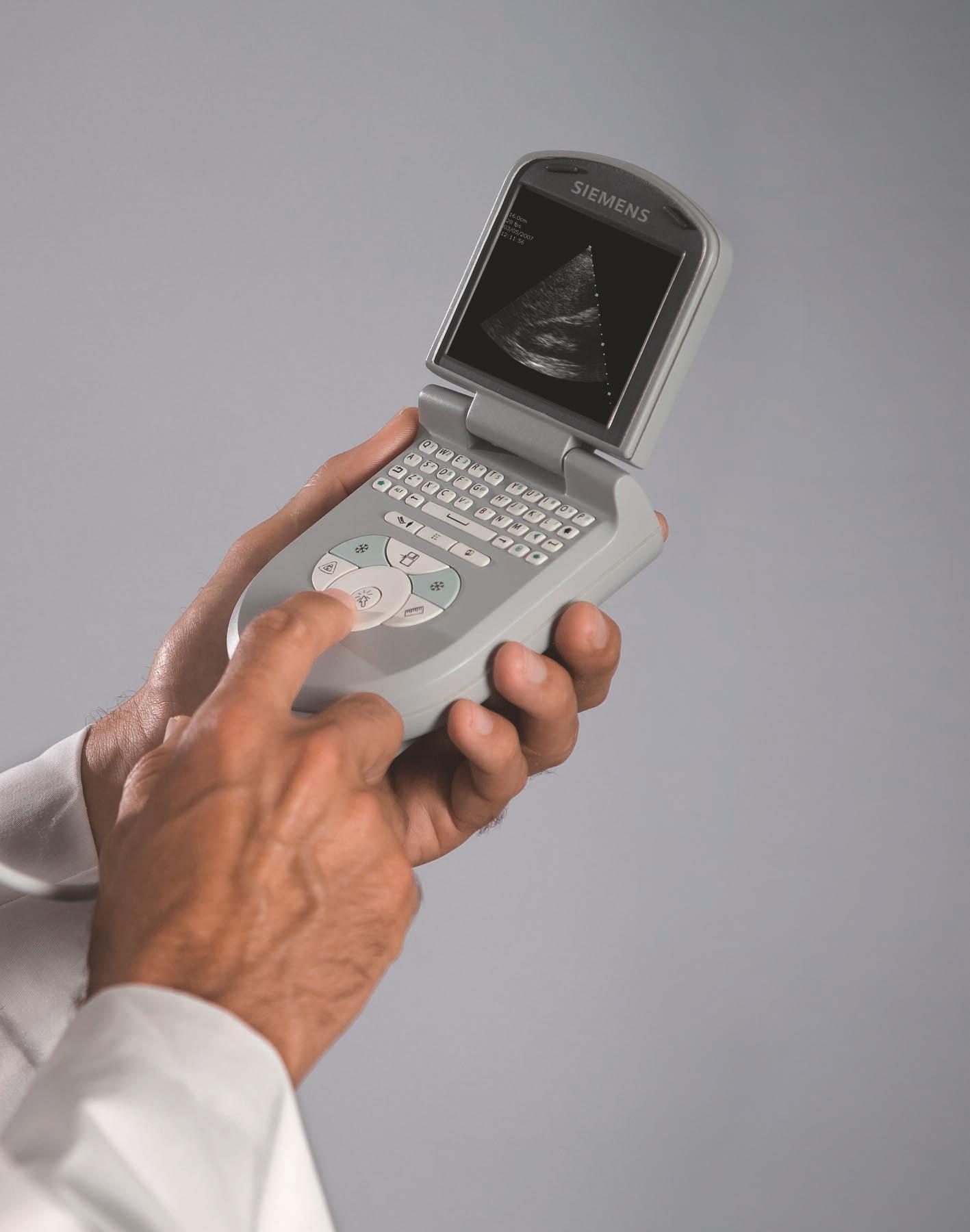
The ACUSON P10 ultrasound system was the world’s first pocket ultrasound device, a hand-held diagnostic and screening tool for physicians, nurses, EMT’s and clinical professionals.

2009
A highly advanced ultrasound system, the ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner obtains high-resolution volumetric images of the breast.
Ideal for use in women with dense breast tissue, it allows the visualization of the anatomical coronal view of the breast. The semi-automated acquisition of volume images helps to reduce operator variability, producing consistent, easily reproducible images.

2009
ACUSON SC2000 is the first echocardiography system to acquire real-time, full volume images of the heart in one heart cycle, delivering a plethora of automated measurements tools that improve the quality of care.

Interscalene Block Catheter Placement using the ACUSON Freestyle system
2012
The ACUSON Freestyle ultrasound system is the world’s first ultrasound system to feature wireless transducers, eliminating the impediment of cables in ultrasound imaging. Introduced in 2012, the system expands the use of ultrasound into interventional and therapeutic applications that require sterile environments. Wireless transducers also expand ultrasound into new and emerging applications, such as administering nerve blocks, enhancing vascular access, and improving target localization through ultrasound guidance during therapeutic interventions and biopsies.

2015
ACUSON SC2000 Prime Edition is one of the first to offer live full-volume color Doppler imaging of heart valve anatomy and blood-flow using a new true volume transesophageal echo (TEE) probe.

2015
ACUSON S Family, HELX Evolution with Touch Control designed with a dedicated focus on the user experience. These new ultrasound image processing systems created new levels of workflow efficiency, imaging performance, and sustainability.
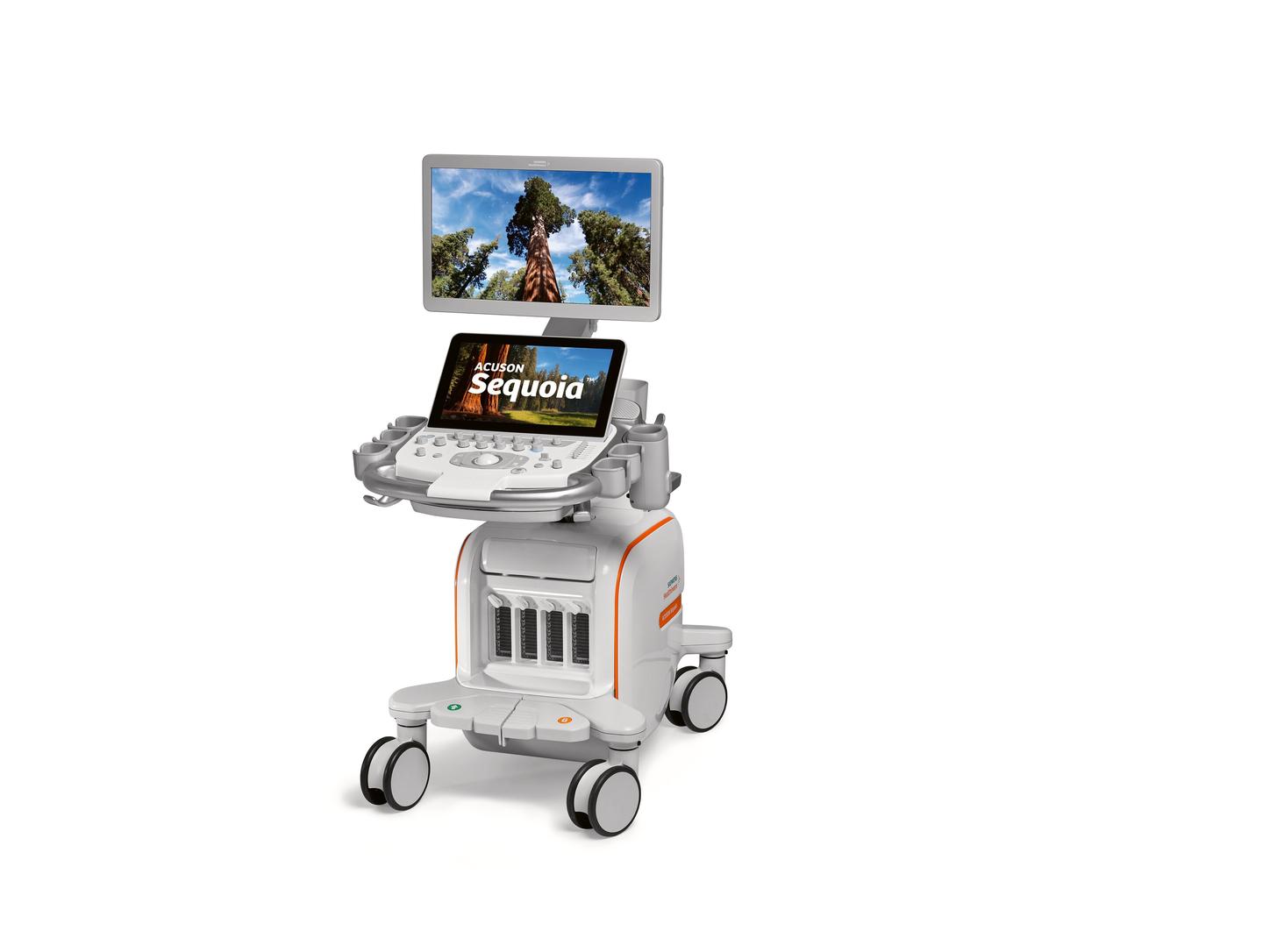
2018
Introduced a new era in ultrasound - ACUSON Sequoia with BioAcoustic™ imaging technology that helps obtain diagnostically relevant images at depths never before thought possible.
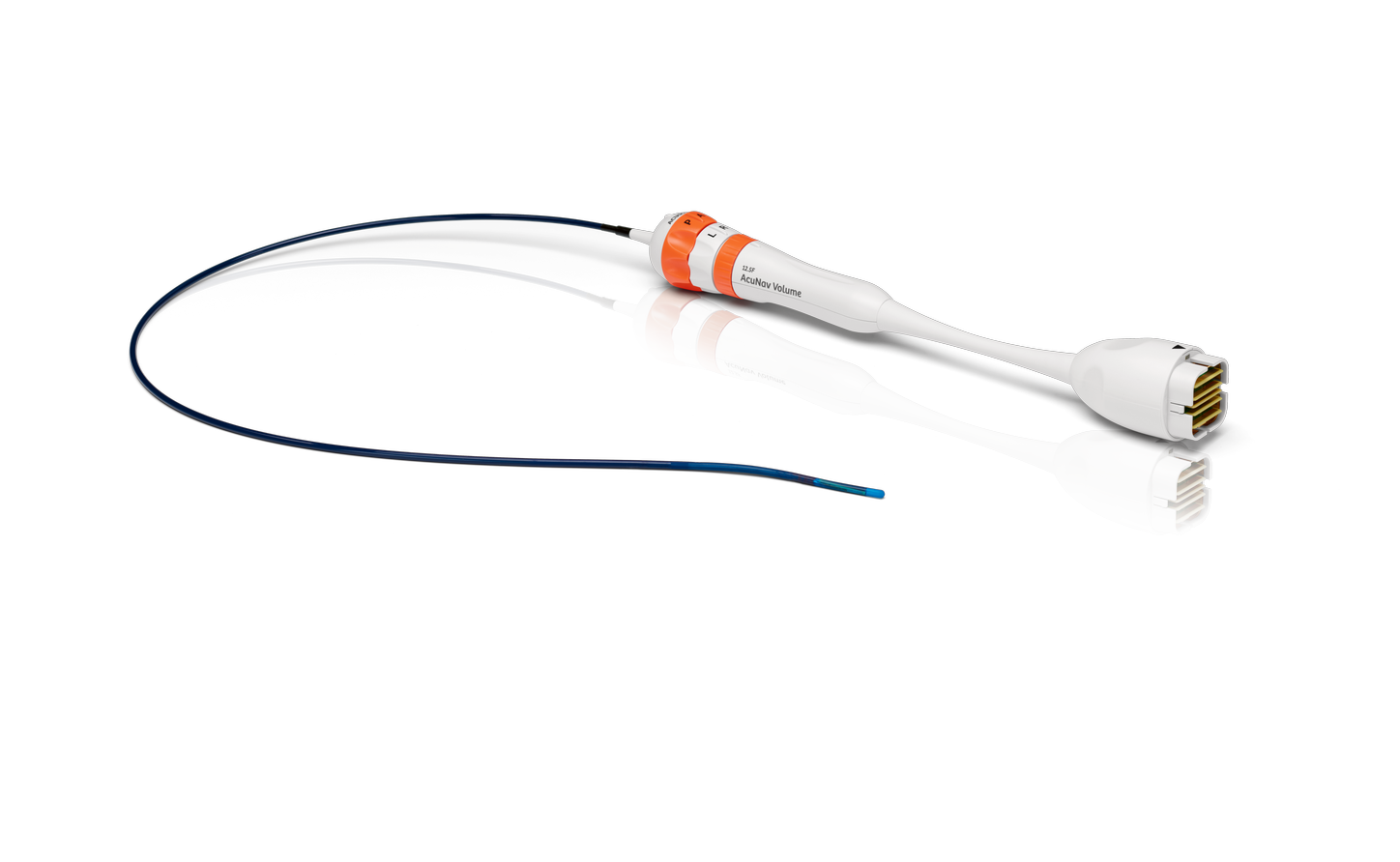
2021
AcuNav Volume ICE Catheter is the world’s first commercially available Volume ICE catheter.