- Hem
- Laboratory Diagnostics
- Assays by Diseases and Conditions
- Diabetes
- A Diabetes Overview: Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Testing

A Diabetes Overview: Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Testing
Educational Resources for Diabetes Awareness
Around the world, approximately 537 million adults (20–79 years) are living with diabetes.
By 2045, this number is projected to rise to over 780 million. More than 1.2 million children and adolescents (0–19 years) are living with type 1 diabetes.1
Almost 1 in 2 adults living with diabetes are undiagnosed.1 Many of those who are undiagnosed may have or be at risk of prediabetes, and recent research has shown that some long-term damage to the body, especially the heart and circulatory system, may already occur in people with prediabetes.2
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, so must the effort to raise awareness. Early detection and monitoring can help minimize complications caused by chronically elevated glucose levels.
Ready to learn more about diabetes?

Webinar
Hemoglobin A1c measurement and standardization
The HbA1c test is used routinely to monitor glycemic control in diabetic individuals and diagnose diabetes. Dr. Randie Little, an expert in HbA1c laboratory testing discusses the importance of HbA1c testing in diagnosing diabetes, its measurement, and the standardization process.

Webinar
Diabetes—Beyond HbA1c
Join Dr. Youssef Maakaroun, MD, as he discusses the various conditions associated with diabetes and how innovative assays can help optimize management of diabetes patients and route them for proper care.

Webinar
Diabetes and obesity—a personalized intervention approach
Dr. Carlos Mendez, a diabetes care expert, discusses how a multidisciplinary approach, including lifestyle changes and regular HbA1c testing, is often needed in the management of patients with uncontrolled diabetes and obesity.
Diagnosing Diabetes
How is diabetes diagnosed?
A diabetes diagnosis is made primarily by the detection of hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar. There are many tools, however, in the array of diabetes-related diagnostic tests.
Types of diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
- Formerly called “insulin-dependent” or “juvenile-onset” diabetes.
- An autoimmune disease that causes destruction of pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for synthesizing and secreting insulin.
- Accounts for 10 % of all diabetes patients.1
Type 2 Diabetes
- Formerly called “non-insulin-dependent” or “adult-onset” diabetes.
- Caused by insulin resistance or inadequate insulin secretion.
- Accounts for 90-95% of all diabetes cases.2
Pre-diabetes
- Patients have impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose.
- Individuals have blood glucose levels higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
- People with pre-diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.3
Monitoring Diabetes
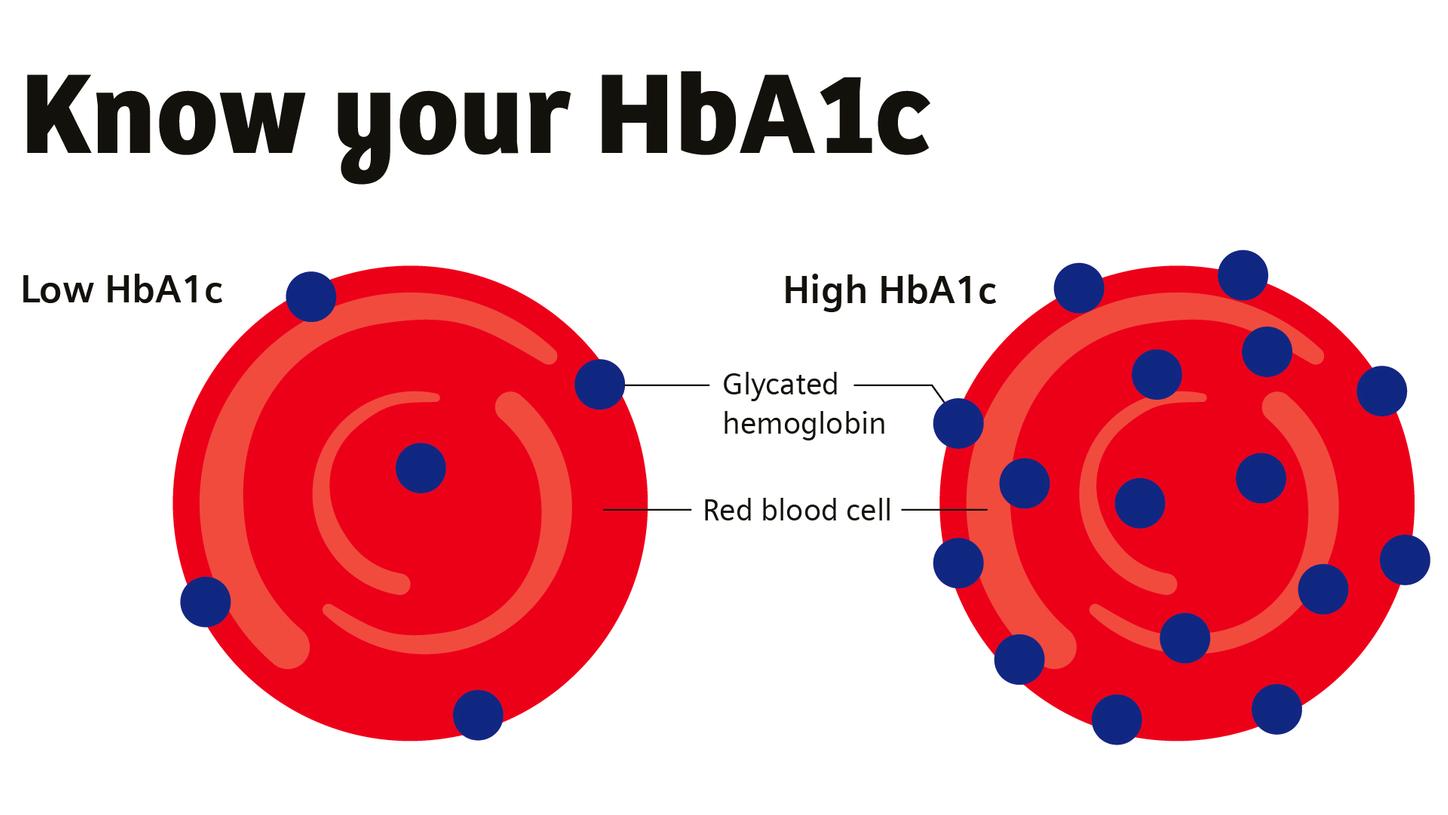
Those diagnosed with diabetes are encouraged to monitor their condition on a regular basis. By measuring hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), doctors can gauge the average blood sugar levels over the last 2–3 months and thereby provide a more tailored treatment plan. HbA1c measurement can also show whether treatment plans and lifestyle choices have been effective.
From a wide range of laboratory assays to comprehensive point-of-care (POC) testing solutions, Siemens Healthineers helps aid clinicians in the differentiation of type 1 from type 2 diabetes, monitor glycemic control and HbA1c levels to follow the progression of the disease, and check for diabetes-related conditions.
Related Conditions

Get the stats about other diseases and conditions related to diabetes! Download the complete infographic below.
Diabetes can pose several long-term health risks
Diabetes is usually accompanied by other conditions, which is why early detection and monitoring is crucial for better patient outcomes.
- Kidney disease, for which diabetes is a leading cause.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects the majority of type 2 diabetes patients.
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure) and cardiovascular disease which could lead to heart attack or stroke.
- Eye problems which could lead to blindness.
- Sores and infections on feet and skin which could lead to amputation.
- Nerve problems can develop at any time, but risk rises with age and longer duration of diabetes.
Video: NAFLD/NASH prevalence in type 2 diabetes patients and use of noninvasive tests
Video: NAFLD/NASH prevalence in type 2 diabetes patients
Diabetes Testing
Why are diabetes-related tests performed?
Diabetes-related tests are performed for various reasons on many different types of patients:
- Newly diagnosed diabetes patients: To help determine if they have type 1 or type 2 diabetes when the clinical indications are inconclusive.
- Type 2 diabetes patients: To monitor and adjust therapies.
- All diabetes patients: To test for diabetic nephropathy by measuring their urinary albumin levels.
- Postmenopausal women: Studies indicate that this group may have an increased risk for cardiac mortality if they have an elevated urinary albumin level.
- Women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome: This syndrome affects 6–10% of all women, with 50% having insulin resistance. These women are at high-risk for developing type 2 diabetes. An abnormally elevated insulin level with hyperglycemia could indicate insulin resistance.
Diabetes and COVID-19

Webinar
Demystifying HbA1c POC testing and the impacts of COVID-19 on patients with diabetes
Dr. Erna Lenters-Westra, Emma English, and Professor Garry John share their insights on the subject of HbA1c POC testing.

MLO Article
Importance of hemoglobin A1c testing for diabetes diagnosis and management post-COVID-19 infection (2023)
Early identification and treatment of the disease can improve health outcomes by avoiding or delaying long-term diabetic complications.

Webinar
During this discussion of diabetes in the context of Covid-19, Dr. Kaufman will explain why HbA1c testing is even more important in today’s healthcare landscape and explore the hypotheses and pathophysiology behind this recent trend.
Attendees are entitled to P.A.C.E. credits from the ASCLS and/or ACCENT credits from the AACC
Public Awareness
November 14 is World Diabetes Day
Each November, Siemens Healthineers works to raise awareness about diabetes—a serious chronic condition, but manageable when detected early enough to begin a physician-monitored treatment plan. We are passionate about helping patients lead healthy lives and partnering with nurses and clinicians to aid them in managing their patients’ conditions.

E-book: Make a difference in diabetes awareness
Interactive e-book: Make a difference in diabetes awareness
2. Centers for Disease Control (https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html)
3. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/type-2-diabetes
The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Due to regulatory reasons, their future availability cannot be guaranteed. Please contact your local Siemens Healthineers organization for further details.