History
Diagnosis

Comments
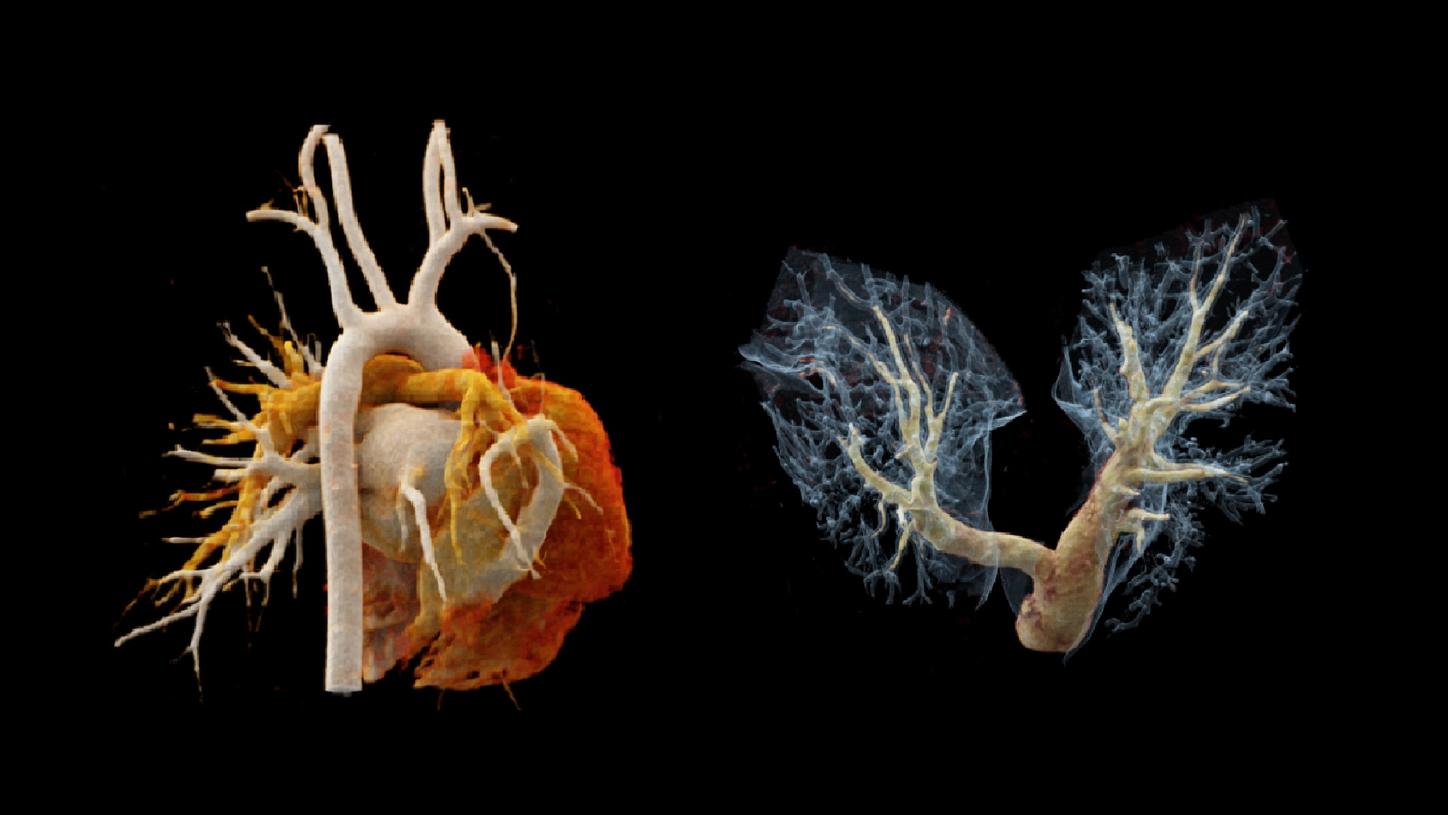
Scimitar syndrome is characterized by the combination of hypoplasia of the right lung and abnormal venous drainage to the inferior vena cava.[1] The syndrome comprises a wide spectrum of symptoms, making the diagnosis difficult, particularly in children and young adults with concomitant congenital cardiac and pulmonary anomalies. Surgical correction is usually carried out on symptomatic patients or on patients with an increased pulmonary blood flow and signs of right heart chamber dilation.[2] Imaging assessment prior to treatment is mandatory. In this case, a unique ultra-fast CT scan mode granted by dual source CT – “Turbo Flash mode” – is performed to complete a thorax scan in 0.42 s in free breathing. A lower kV setting, of 70 kV, is applied to enhance image contrast, optimizing image quality at a reasonably achievable lower radiation dose and less contrast agent. Three dimensional imaging techniques, such as multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), maximum intensity projection (MIP) and cinematic volume rendering technique (cVRT), offer the potential of higher diagnostic confidence and accuracy, as well as improving communication and planning for treatment.