Computed Tomography for NeurologyInnovation that matters
Our mission is to help neurology patients by best supporting their diagnosis and treatment. We are committed to providing you with fast and reliable CT imaging to make informed treatment decisions. They are, of course, particularly important in stroke, where time is brain. More than 6.5 million people die from stroke each year and more than 100 million people are currently living with the consequences of stroke, ranging from moderate to severe disability1.
We firmly believe that innovation in computed tomography can create great momentum in neuroradiology and neurology. You think ahead in advancing neurology care. We innovate ahead with technologies that support you throughout the entire patient pathway. Discover how state-of-the-art CT technologies by Siemens Healthineers can help you care for your stroke patients.
Stéphane’s Acute Stroke Journey
Follow Stéphane on his individual Journey

Thank you for accompanying Stéphane on his stroke journey. We are grateful that we were able to contribute to his fast diagnosis and successful treatment with our solutions.

One morning, Stéphane collapsed. His wife immediately dialed the emergency number. Stéphane was half-paralyzed on the right side and had trouble talking and understanding. The ambulance came and took him immediately to the hospital.
2 https://www.world-stroke.org/world-stroke-day-campaign/about-stroke/impact-of-stroke

Now let’s have a closer look at the diagnosis and treatment pathway of Stéphane and how through Siemens Healthineers' comprehensive imaging and automated zero-click post-processing solutions, he got a second chance in life.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
As a first step to assess the severity of the stroke, the NIH Stroke Scale assessment was conducted to measure the neurological function and deficits. The assessment revealed a score greater than 6.
The next step was performing an immediate native CT scan. Hemorrhage was ruled out and the AI-based Brain Hemorrhage* detection application, which runs directly on the scanner, concluded the analysis without raising any flags for suspected brain hemorrhage.
Meanwhile the high contrast-to-noise ratio of the native head CT scan, ensures that subtle nuances that are indicative of early signs of ischemia are visualized. Hypodense regions were noticed on the right hemisphere, indicating areas with early signs of suspected ischemia.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
To detect and localize the clot causing the ischemia, intracranial CT Angiography was performed. The acquired images helped the care team to get more insights, where through constructing a maximum intensity projection (MIP) image, an occlusion in the middle cerebral artery is confirmed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
The critical question before going to mechanical thrombectomy is to understand how much core infarct and how much salvage tissue there is. This can be easily achieved by acquiring a CT brain perfusion scan.
Using Flex-4D spiral acquisition on our SOMATOM X.cite* scanner enables a temporal sampling of 1.5 sec and 10 cm coverage, ensuring the full coverage of the supratentorial area and protecting the eye lenses.
After the scan, the perfusion maps were automatically generated with zero-click interaction from the radiologist. Based on this information a penumbra map was calculated with an encouraging mismatch ratio. The care team decided to send Stéphane to the Angio suite for thrombectomy.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Stéphane is now sent to the angio suite for thrombectomy

Device navigation with Neuro device protocol during thrombetomy
Roadmap:
Create your own guide
- Vessel map to ease catheter and device navigation
- Constant image quality through the whole procedure
- Supported by functionalities like “show progress” or “vessel map” to ease your procedure workflow
DSA Roadmap:
- Select any DSA reference image as roadmap mask
- Increase image quality of vessel map
- Use already acquired DSA scene
- Reduce dose by skipping dedicated vessel map acquisition for roadmap

Fortunately, the thrombectomy procedure was successful with an excellent outcome, providing Stéphane with a second chance in life.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
24h later – follow-up imaging
To detect potential hemorrhagic transformations, a 24-hour follow-up scan was conducted, where SOMATOM On.site* mobile CT scanner was used to scan the patient directly at his bed in the ICU department. The native CT scan showed some hyperdense regions, which indicates whether a hemorrhage or contrast extravasation post thrombectomy. To get the definite answer, the care team decided to go for a Dual Energy CT scan at the radiology department. Hyperdense regions were reconfirmed with the first native CT scan.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
Thanks to the dual energy CT imaging capabilities, it is now easy to get the answer!
The iodine maps comparing hyperdense spots with areas of negativity on the virtual non-contrast (VNC) reconstruction indicate that the hyperdense spots were due to contrast extravasation not a hemorrhage.

Thank you for accompanying Stéphane on his stroke journey. We are grateful that we were able to contribute to his fast diagnosis and successful treatment with our solutions.

One morning, Stéphane collapsed. His wife immediately dialed the emergency number. Stéphane was half-paralyzed on the right side and had trouble talking and understanding. The ambulance came and took him immediately to the hospital.
2 https://www.world-stroke.org/world-stroke-day-campaign/about-stroke/impact-of-stroke

Now let’s have a closer look at the diagnosis and treatment pathway of Stéphane and how through Siemens Healthineers' comprehensive imaging and automated zero-click post-processing solutions, he got a second chance in life.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
As a first step to assess the severity of the stroke, the NIH Stroke Scale assessment was conducted to measure the neurological function and deficits. The assessment revealed a score greater than 6.
The next step was performing an immediate native CT scan. Hemorrhage was ruled out and the AI-based Brain Hemorrhage* detection application, which runs directly on the scanner, concluded the analysis without raising any flags for suspected brain hemorrhage.
Meanwhile the high contrast-to-noise ratio of the native head CT scan, ensures that subtle nuances that are indicative of early signs of ischemia are visualized. Hypodense regions were noticed on the right hemisphere, indicating areas with early signs of suspected ischemia.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
To detect and localize the clot causing the ischemia, intracranial CT Angiography was performed. The acquired images helped the care team to get more insights, where through constructing a maximum intensity projection (MIP) image, an occlusion in the middle cerebral artery is confirmed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
The critical question before going to mechanical thrombectomy is to understand how much core infarct and how much salvage tissue there is. This can be easily achieved by acquiring a CT brain perfusion scan.
Using Flex-4D spiral acquisition on our SOMATOM X.cite* scanner enables a temporal sampling of 1.5 sec and 10 cm coverage, ensuring the full coverage of the supratentorial area and protecting the eye lenses.
After the scan, the perfusion maps were automatically generated with zero-click interaction from the radiologist. Based on this information a penumbra map was calculated with an encouraging mismatch ratio. The care team decided to send Stéphane to the Angio suite for thrombectomy.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Stéphane is now sent to the angio suite for thrombectomy

Device navigation with Neuro device protocol during thrombetomy
Roadmap:
Create your own guide
- Vessel map to ease catheter and device navigation
- Constant image quality through the whole procedure
- Supported by functionalities like “show progress” or “vessel map” to ease your procedure workflow
DSA Roadmap:
- Select any DSA reference image as roadmap mask
- Increase image quality of vessel map
- Use already acquired DSA scene
- Reduce dose by skipping dedicated vessel map acquisition for roadmap

Fortunately, the thrombectomy procedure was successful with an excellent outcome, providing Stéphane with a second chance in life.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
24h later – follow-up imaging
To detect potential hemorrhagic transformations, a 24-hour follow-up scan was conducted, where SOMATOM On.site* mobile CT scanner was used to scan the patient directly at his bed in the ICU department. The native CT scan showed some hyperdense regions, which indicates whether a hemorrhage or contrast extravasation post thrombectomy. To get the definite answer, the care team decided to go for a Dual Energy CT scan at the radiology department. Hyperdense regions were reconfirmed with the first native CT scan.
* The products/features (mentioned herein) are not commercially available in all countries. Their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Image courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
Thanks to the dual energy CT imaging capabilities, it is now easy to get the answer!
The iodine maps comparing hyperdense spots with areas of negativity on the virtual non-contrast (VNC) reconstruction indicate that the hyperdense spots were due to contrast extravasation not a hemorrhage.

Thank you for accompanying Stéphane on his stroke journey. We are grateful that we were able to contribute to his fast diagnosis and successful treatment with our solutions.











Redefine neurology CT
We are innovating ahead to help you advance the role of CT in neurology. For example, our breakthrough photon-counting technology offers a new level of anatomical detail. Say goodbye to the trade-off between resolution and dose – and confidently perform scans that were not practicable before.
Redefining imaging at the front line of stroke care
NAEOTOM Alpha has eclipsed conventional high-end CT scanners at the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Hear from Anke van der Eerden, MD, and the team how ultra-thin slice thickness has enabled a whole new level of detail while keeping dose to a minimum.
Fast stroke assessment with NAEOTOM Alpha
Hear from Tobias Granberg, MD, from Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, how photon-counting CT is expanding the boundaries of neuroradiology. In this video he showcases how a complete triple rule-out and stroke assessment without the need for ECG was conducted in < 6.5 minutes.
Detect smaller structures with high precision
Watch the video above to learn how the high resolution of photon-counting CT can provide further insights in temporal bone, ear implants, and CSF imaging. The cases are presented by Tim Amrhein, MD, from Duke University Medical Center, USA.
Customer voices
When time is of the essence, smart solutions can make a difference. Discover how our cutting-edge CT technologies have driven efficiency, productivity, and precision at the institution of our customer.
Hybrid CT-angio systems at the nexus of treatment innovation
Our hybrid interventional suite enables challenging multi-modality procedures and streamlines workflows. At Vall d’Hebron Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, Carlos Molina, MD, and Alejandro Tomaselli, MD, have shortened the door-to-groin time to less than 30 minutes. Learn more about this important step in improving patient outcomes.
Identifying post-treatment complications quickly and easily
Designed to achieve fast and reliable head CT images, SOMATOM On.site is a portable CT system that provides access to the known SOMATOM image quality, right at your patient’s bedside. Watch Johan Wasselius, MD, from Lund University Hospital, Sweden, explain how SOMATOM On.site helps them reduce transports, thus saving valuable time and staff resources.
Clinical cases

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Follow-up head CT scan in the ICU after a severe brain injury
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 44.1 mGy

Courtesy of Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary
Visualize dislocated inner ear prosthesis in Quantum HD
Quantum HD | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 15.5 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
CT angiography of the cerebral arteries
CTDIvol 8.5 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Follow-up patient after clipping
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 8.17 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 180 mGy

Courtesy of Duke University Medical Center, USA
Shown in: Madhavan et al. (2023). https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a7887
Visualize small CSF-venous fistulas with Quantum HD and enable treatment options
0.2mm | 120 kVp | DLP 442 mGy*cm

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Visualize micro-calcifications in ophthalmic and superficial temporal arteries
Quantum HD | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 10 mGy | DLP 375 mGy*cm

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Support stroke assessment with low kv imaging and zero-click thanks to Recon&GO
Native: 120kVp | CTDIvol 42 mGy – CTA 70kVp | CTDIvol 2.96 mGy – CT Perfusion 70kVp | CTDIvol 103 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Stroke Patient Assessment
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 40.07 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 158.11 mGy | CT Angiography: 90kVp | CTDIvol 7.07 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Complete stroke assessment with native brain scan, supra-aortic CTA and brain perfusion
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 41.07 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 158.11 mGy | Carotid CTA: 90kV | CTDIvol 7.07 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Visualization of iodine uptake with syngo.CT DE Brain Hemorrhage
TwinSpiral Dual Energy CT: 80/Sn150 KV | CTDIvol 37.06 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Ultra high-resolution inner ear without dose penalties thanks to Tin Filter
Sn130 kV | CTDIvol 24.07 mGy
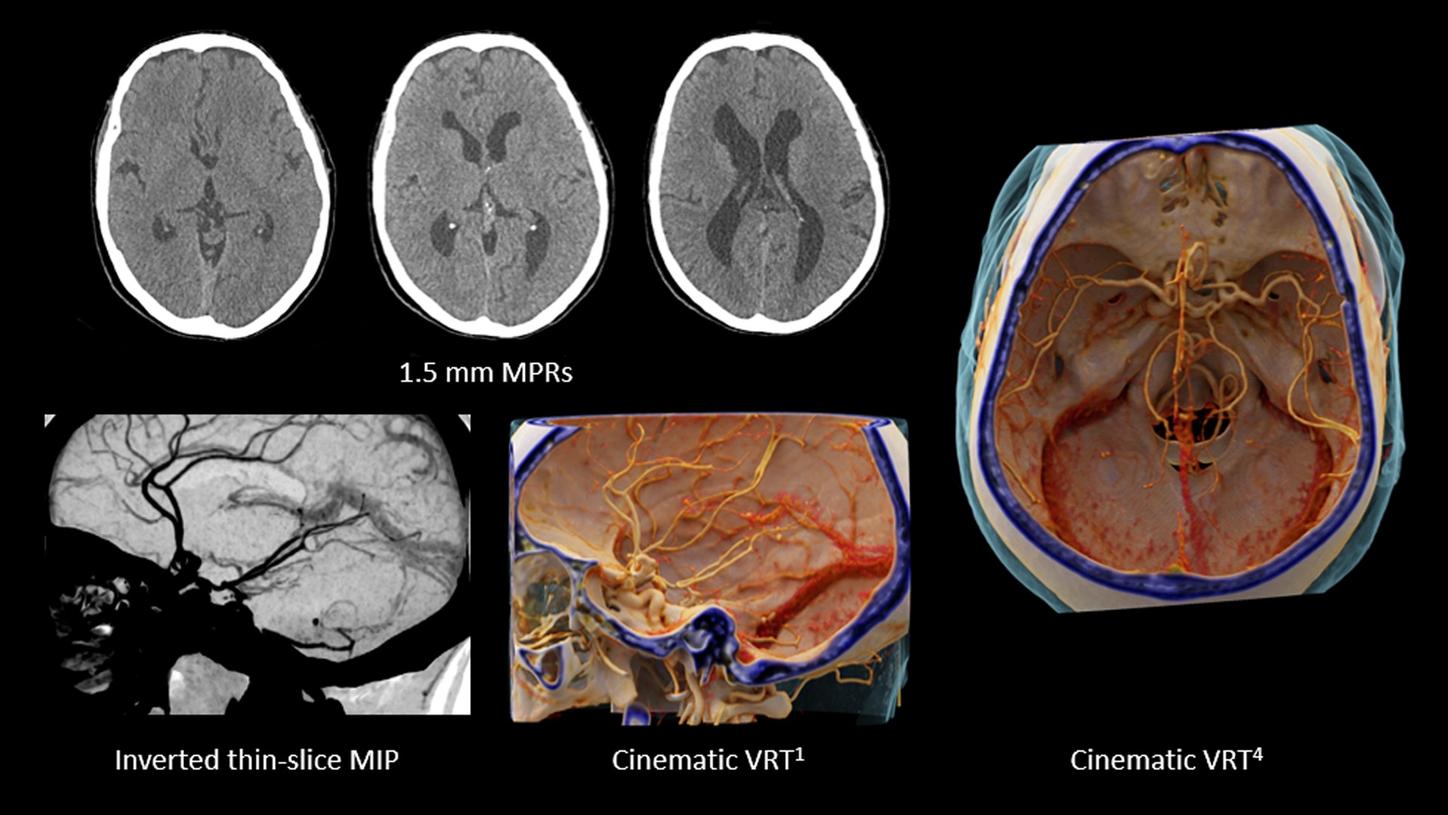
Courtesy of Centro Hospitalar e Universitario de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Rule-out of bleeding and vascular status clarification
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 38.4 mGy | CTA: 80kV | CTDIvol 6.3 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Follow-up head CT scan in the ICU after a severe brain injury
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 44.1 mGy

Courtesy of Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary
Visualize dislocated inner ear prosthesis in Quantum HD
Quantum HD | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 15.5 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
CT angiography of the cerebral arteries
CTDIvol 8.5 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Follow-up patient after clipping
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 8.17 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 180 mGy

Courtesy of Duke University Medical Center, USA
Shown in: Madhavan et al. (2023). https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a7887
Visualize small CSF-venous fistulas with Quantum HD and enable treatment options
0.2mm | 120 kVp | DLP 442 mGy*cm

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Visualize micro-calcifications in ophthalmic and superficial temporal arteries
Quantum HD | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 10 mGy | DLP 375 mGy*cm

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Support stroke assessment with low kv imaging and zero-click thanks to Recon&GO
Native: 120kVp | CTDIvol 42 mGy – CTA 70kVp | CTDIvol 2.96 mGy – CT Perfusion 70kVp | CTDIvol 103 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Stroke Patient Assessment
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 40.07 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 158.11 mGy | CT Angiography: 90kVp | CTDIvol 7.07 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Complete stroke assessment with native brain scan, supra-aortic CTA and brain perfusion
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 41.07 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 158.11 mGy | Carotid CTA: 90kV | CTDIvol 7.07 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Visualization of iodine uptake with syngo.CT DE Brain Hemorrhage
TwinSpiral Dual Energy CT: 80/Sn150 KV | CTDIvol 37.06 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Ultra high-resolution inner ear without dose penalties thanks to Tin Filter
Sn130 kV | CTDIvol 24.07 mGy

Courtesy of Centro Hospitalar e Universitario de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Rule-out of bleeding and vascular status clarification
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 38.4 mGy | CTA: 80kV | CTDIvol 6.3 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Follow-up head CT scan in the ICU after a severe brain injury
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 44.1 mGy












Did this information help you?
Thank you.
The statements by Siemens Healthineers’ customers described herein are based on results that were achieved in the customer's unique setting. Because there is no "typical" hospital or laboratory and many variables exist (e.g., hospital size, samples mix, case mix, level of IT and/or automation adoption) there can be no guarantee that other customers will achieve the same results.

